Retinal O2 Saturation & Glaucomatous VF Defects
The Journal of Glaucoma recently published findings which found a counterintuitive relationship but significant correlation between retinal oxygen saturation (StO2) and the severity of visual field loss in glaucoma patients.
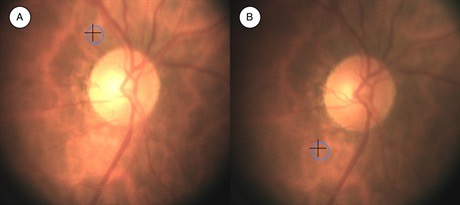
A study utilizing novel diffuse reflectance spectroscopy found higher StO2 levels in retinal tissue were surprisingly associated with worse visual field mean deviation (MD) scores. Specifically, each 1% increase in StO2 corresponded to a 0.06 dB loss in MD, even after controlling for intraocular pressure and central corneal thickness. This relationship was particularly pronounced in the superior visual field, therefore also suggesting an anatomic link with the inferior disc and retinal nerve fiber layer. The finding indicates elevated StO2 likely reflects reduced oxygen consumption in glaucomatous tissue, which in turn creates a compensatory mechanism of increased O2 perfusion.
While these results don't exclude ischemia as a contributing factor to glaucomatous optic neuropathy, the finding offers an interesting insight into metabolic changes occurring in the pathophysiology of glaucoma and may provide a new biomarker in the future for disease progression and management.
-JRM
Go to the article in Journal of Glaucoma
HELP BUILD THE DIGITAL COURSE ACADEMY
Have a course to submit or idea for a course? Reach out!
Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care Now LIVE!
- Downloadable Book & Companion Course
- Modular "Go At Your Own Pace" Format
- 2 CE's & Instant Certificate
- Med-Eye Minute QAM Newsletter
- Innovative Learning Platform & Community
READ THE BOOK SERIES ON AMAZON
Kindle, Paperback, & Hardcover Now Available



Responses